2.7 Connection of 3K-radiation and energy of bonding of the hydrogen-molecule
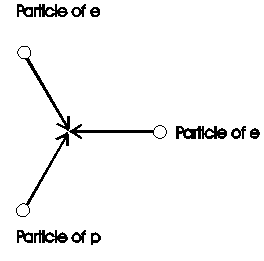
To view also complex structures on the base of particles, is here calculated the energy of bonding of the hydrogen-molecule. In /2-12/ is give the bonding-energy to 432 kJ/mol. This number shall now derived from the 3K-radiation. In chapter 2.1.3 and figure 2.1.3-1 is descript the transition from the structure of the proton to the structure of the electron. One particle, coming from the proton, is collide with two particles from the electron (Fig. 2.7-1).

Fig. 2.7-1: Connection of proton p with its electron e: Shown is the collision of one particle from the proton with two particles its electron during the generation of a structure.
For two hydrogen-atoms follow figure 2.7-2.

Fig. 2.7-2: Generation of a structure on the hydrogen-atom 1 (proton p1) and generation of the structure on the hydrogen-atom 2 (proton p2) before the combining to a molecule
At the formation of a molecule of hydrogen H2 are energy free, i.e. structure (what can market as mass too) is not further need. The economized particles are market red in figure 2.7-2.
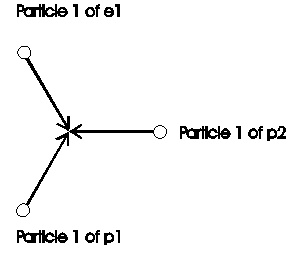
Fig. 2.7-3: Structure in a hydrogen-molecule after assemble from atoms
Here was 3 particle economized: Particle 2 from e1
Particle 1 from e2
Particle 2 from e2
These three economized electron-particles represent a specified part of mass (part of structure) of the electron. The are free energy of bond is consequently calculable from the number of economized particles in relation to all particles of an electron:
![]()
2.7-1
(Still is treated under bond-energy only the for one molecule.)
The bond-energy for one molecule is
named ![]() .
.
The total-energy of the electron is:
![]()
The number of economized particles at the bond is 3.
The total number of electron-particles is in chapter 2.1.2 (named “NAttempt as number of participated particles on the structure”) declared as:
![]() 2.7-2
2.7-2
With that follow equation above, valid for one molecule:
![]() 2.7-3
2.7-3
For one mol of molecular hydrogen is
![]() to multiply with the constant of
Avogadro
to multiply with the constant of
Avogadro ![]() .
.
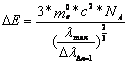 2.7-4
2.7-4
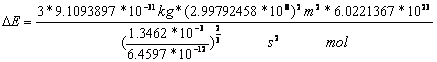 2.7-5
2.7-5
![]() 2.7-6
2.7-6
Deviation:-2.6%