2. Quantitative connections
2.1 The connection of the 3K-radiation and the mass of the electron
2.1.1 Level of knowledge
Because I not have new knowledge for the structure and mode of action of the electron, fall back on the conception from 2003 (see draft of 2003, page 19: “From the structure of the electron to its mass”). The conception for the structure and mode of action of the electron are speculative, as each search to a new way. But because they have delivered useful numerical value, they was not rejected. However the structure and the mode of action of the electron represent a position of key and are therefore interest in the future.
In the following chapter are used next to the deduce of the formulas and next to the numerical values from 2003. The corrected number of values for λmax and ∆λ∆n=1 (see chapter 1.4) are set in only then at the end of the execution. They lead to a pleasing improvement of the exactness.
2.1.2 The discovery of the connection between the 3K-radiation of the cosmos and the de-Broglie-wave-length of the electron
It was plant in the first instance only
to introduce the redshift, the diffraction of the light and chiefly the constant
of gravitation as utilization of this theory. Latest become apparent but not
solving without near view to the connection of radiation and mass. For these
view look the electron a suitable object, because it is narrow link to
radiation. It give us the light. Of interest is the structure of the electron,
based on the particles. Thence was searched the connection between the structure
of the electron based on particles and its mass. To reach the mass, select the
way about the energy. To reach the energy must to determine the number of
elements of energy from type
![]() and here length of wave.
and here length of wave.
It was run trough 5 parts and it was as the search a way in mist:
1. Part
Assumption: The structure based on 4-particle-collision and therefore it is tree-dimensional (Fig. 2.1.2-1):
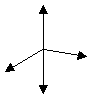
Fig 2.1.2-1: 4-particle-collision
Because 3-particle-collisions happen often than 4-particle-collisions, this structure was not pursue forward. Besides this 3-collision-structure in plane form harmonize better between the 3K-space, on what they can supported, and between the structure of the nucleus, what is a 4-particle-collision probably.
2.Part
Assumption: The structure based on a 3-particle-collision (Fig. 2.1.2-2):
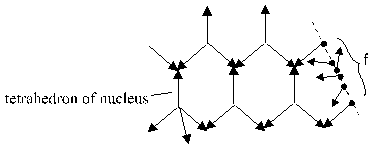
Fig. 2.1.2-2: Assumed structure of nucleus and electron
3. Part
The distance f must so large, that in relation to the supported particles, what coming out the 3K-space, an agreement exist with the 3K-space.
4. Part
Estimation of
f:
To fill the
condition of the ![]() (3 particle with determined
distance and determined direction), are need the number
(3 particle with determined
distance and determined direction), are need the number
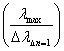 of steps according to fig. 2.1.2-3.
of steps according to fig. 2.1.2-3.
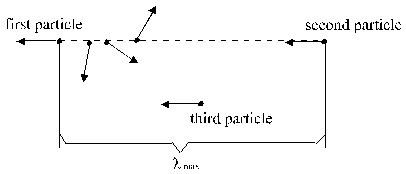
Fig. 2.1.2-3: Number of steps to length of wave λmax
![]() 2.1.2-1
2.1.2-1
Notation:
These numerical values results from that values, what used in the first instance
with T=3 K and ![]() (from
(from
![]() ) /2-1/ 2.1.2-2
) /2-1/ 2.1.2-2
But later in the specifying was used the values from COBE, where was the base at the arrangement too.
It make one
hit ![]() with
with
![]() attempts.
attempts.
Demonstrate in probabilitys:
The designate condition: „3 particles with determinate distance and determinate direction“ can write as:
Ž
[The first particle has the direction"![]() " and the determinate distance to
particle 2]
" and the determinate distance to
particle 2]
=
Probability p1
Ž
[The second particle has the direction"![]() "and the determinate distance to
particle 3]
"and the determinate distance to
particle 3]
= Probability p2
Ž
[The third particle has the direction"![]() "and the determinate distance to
particle 1]
"and the determinate distance to
particle 1]
=
Probability p3
[Probability
for the hit for ![]() ]
]![]()
2.1.2-3
For the conditions of estimate of f apply to(Fig. 2.1.2-4):
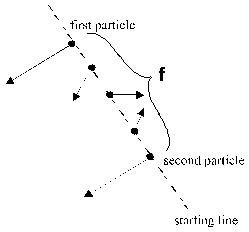
Fig. 2.1.2-4 Detail from fig. 2.1.2-2
Ž
[The first particle has the direction"![]() " and the determinate distance to
particle 2]
= Probability p1
2.1.2-4
" and the determinate distance to
particle 2]
= Probability p1
2.1.2-4
Ž
[The second particle has the direction"![]() "and the determinate position to
particle 1]
= Probability p2
"and the determinate position to
particle 1]
= Probability p2
2.1.2-5
(at which "determinate position" here mine "Line of start")
One hit result after
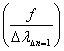 attempts.
attempts.
The probability is:
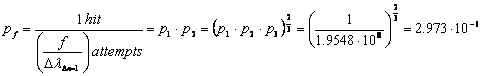
2.1.2-6
respectively
the number of attempts ![]() 2.1.2-7
2.1.2-7
With that is
![]() 2.1.2-8
2.1.2-8
![]() 2.1.2-9
2.1.2-9
5. Part:
Number of
elements of the structure (element of the type
![]() , i.e. three particle as in the
photon)
, i.e. three particle as in the
photon)
Under that next to: Number of particles, who take part on the structure:
(see fig. 2.1.2-2)
The structure of the electron be made of a number of particles, where support inside on the nucleus and outside on the 3K-space. It can take so much structure-particle on the structure, till in statistical average a destruction of these structure by a 3-particle-collision followed. For these must have two extraneous particle a defined distance and a defined direction to the target-particle of the structure.
These is but the same condition, what used for the estimation of f (Fig 2.1.2-5).
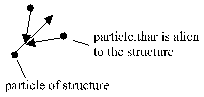
Fig.: 2.1.2-5 Destruction of a structure
With these is
a structure, what is support on a nucleus, after
![]() attempts, mean particles of the
structure of the electron, destructed in average. That is not depend on the form
of the structure.
attempts, mean particles of the
structure of the electron, destructed in average. That is not depend on the form
of the structure.
It is possible, that on each of peak of tetrahedron supported two structures (Fig. 2.1.2-6):
![]()
Fig.2.1.2-6: Support of the structure of the electron on the peak of the tetrahedron
The number of particles is so: : 4*2*3.363*105.
Now to the number of elements from type λ :
An element from type λ need as each photon three particle. Therefore to make from these number of particles groups of three particles (Photons of three particles).
Result 8.97*105 groups.
Now to length of wave of the elements from type λ:
For length of wave λ of these group of three particle offer f, because the directions of the particles 1 and 2 as to see in fig. 2.1.2-4 too can exist as in fig. 2.1.2-7:
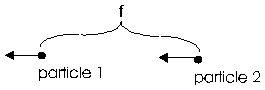
Fig. 2.1.2-7: Direction of the particle 1 and 2 changed opposite to fig. 2.1.2-4
![]() 2.1.2-10
2.1.2-10
With that are number and length of wave of the elements available.
The energy of
the structure is with that :
![]() 2.1.2-11
2.1.2-11
The mass
![]() 2.1.2-12
2.1.2-12
Because these
value is very near to the mark
![]() , are the numerals in the equation
above replaced by their symbols, to see clear the physical content:
, are the numerals in the equation
above replaced by their symbols, to see clear the physical content:
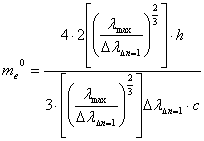 2.1.2-13
2.1.2-13
![]() 2.1.2-14
2.1.2-14
With the exception of the term
![]() represent so surprisingly the
represent so surprisingly the
![]() from the 3K-space the
de-Broglie-length of wave of the electron. Now the
sun shine anew.
from the 3K-space the
de-Broglie-length of wave of the electron. Now the
sun shine anew.
2.1.3 Attempt for specifying of the structure of the electron
The reducing of the number of parts in the numerator (partly) and of the factor of length of wave in the denominator (Equation 2.1.2-13) point at , that can exist different structures of the electron. Therefore was make an effort to specify the structure of the electron:
On the base of a 4-particle-collision of the nucleus is to see the electron as mediator between the nucleus and the 3K-space (see fig. 2.1.3-1):
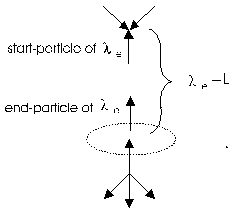
Fig. 2.1.3-1: Effect of support of the electron between nucleus and 3-particle-collision with extraneous particles
The effect of support of the electron reach from nucleus to the destruction by a 3-particle –collision (in mean). Mean, till the particle coming from the nucleus meet two particles, where have estimated direction and the same distance to it as to see in fig. 2.1.2-5. That is after "Nattempt "attempts the case.
 2.1.3-1
2.1.3-1
For each attempt is need a distance of
![]() .With that is the length of support
L of the electron:
.With that is the length of support
L of the electron:
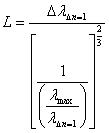 2.1.3-2
2.1.3-2
Because these constellation of the
start-particle and of the end-particle in fig. 2.1.3-1 is the same as comply
with the condition of a ![]() : “Particle 1 in the signet
direction and particle 2 in the signet direction and the distance shall L”, can
to be L the length of wave
: “Particle 1 in the signet
direction and particle 2 in the signet direction and the distance shall L”, can
to be L the length of wave ![]() of the electron.
of the electron.
Now is still to estimate the number
![]() of that
of that
![]() , what belong to a electron.
, what belong to a electron.
A structure can only exist up to a estimated largeness, because than in mean a 3-particle-collision it destructed.
That is the case with equation above at
"Nattempt " as the number of particles, where take place at the
structure. With that is known the number of particles, where build the electron.
Because need three particle for each
![]() , is to divided this number of
particles by 3, to yield the number of
, is to divided this number of
particles by 3, to yield the number of
![]() :
:
 2.1.3-3
2.1.3-3
Based on a structure of 4-particle–collision of the nucleus exist four directions, at which in each direction can build a structure (Fig. 2.1.3-2).:
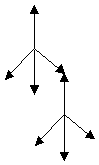
Fig. 2.1.3-2: The four directions of the nucleus
Besides is to consider the followed:
The structure of support of the electron is not only build from particles, where fly in direction out the nucleus. Are need particles with a direction to the nucleus too because a stationary condition. It is not to assume, that the nucleus is unchangeable stable and stationary in the structure. It is rather dynamical and only in mean to see stationary. Therefore go particle through the nucleus, where fly in its direction. With these to add to the four directions of out four directions to in and trough the nucleus.
Follow to calculate with eight fields of the structure:
![]() 2.1.3-4
2.1.3-4
![]()
![]()
 2.1.3-5
2.1.3-5
![]() 2.1.3-6
2.1.3-6
![]() .(Value of 2003 from the maximum of
energy) 2.1.3-7
.(Value of 2003 from the maximum of
energy) 2.1.3-7
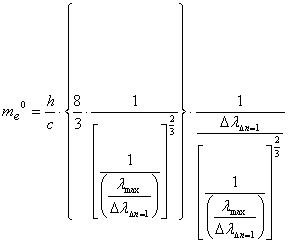
followed the result of 2003:
![]() 2.1.3-8
2.1.3-8
With the value of 2010 for ∆λ∆n=1 =6.4597*10-12 m (from the maximum of the number of photons; see 1.4 “Estimation of the average distance between two particles from the date of 3K-radiation”)followed:
me0= 9.124*10-31kg instead 9.109*10-31kg, deviation:+0.16% 2.1.3-9
The correction of ∆λ∆n=1 lead to a astonishing correction of the exactness.
On the other side is to say, that as the structure as the function of the electron are unknown now as before.